Spring Boot Repository Layer or DAO Layer Integration Testing using Testcontainers
In the previous tutorial, we have seen how to write Integration tests for REST API using Testcontainers.
Prerequisite
Spring Boot Testing - REST API Integration Testing using Testcontainers
Create Integration Tests for Data Access or Repository Layer with MySQL database
Let's first write Integration tests for StudentRepository without using Testcontainers and then later we will use Testcontainers.
Let's create StudentRepositoryTests class and add the following content to it:
package net.javaguides.spirngboot.repository;
import net.javaguides.spirngboot.AbstractContainerBaseTest;
import net.javaguides.spirngboot.entity.Student;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.jdbc.AutoConfigureTestDatabase;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.DataJpaTest;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@DataJpaTest
@AutoConfigureTestDatabase(replace = AutoConfigureTestDatabase.Replace.NONE)
class StudentRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
// JUnit for save student operation - BDD style
@Test
public void givenStudentObject_whenSave_thenReturnSavedStudent(){
// given - setup or precondition
Student student = Student.builder().firstName("Ramesh")
.lastName("fadatare").email("ramesh@gmail.com").build();
// when - action or the testing
Student savedStudent = studentRepository.save(student);
// then - very output
Assertions.assertNotNull(savedStudent);
Assertions.assertNotNull(savedStudent.getId());
}
// JUnit for findById student operation - BDD style
@Test
public void givenStudentId_whenfindbyId_thenReturnSavedStudent(){
// given - setup or precondition
Student student = Student.builder().firstName("Ramesh")
.lastName("fadatare").email("ramesh@gmail.com").build();
Student savedStudent = studentRepository.save(student);
// when - action or the testing
Student studentDB = studentRepository.findById(student.getId()).get();
// then - very output
Assertions.assertNotNull(studentDB);
}
}
The Spring boot provides @DataJpaTest annotation. This annotation will disable full auto-configuration and instead apply only configuration relevant to JPA tests. By default, it will use an embedded, in-memory H2 database instead of the one declared in the configuration file, for faster test running time as compared to disk file database.
Note that we have disabled H2 in-memory database support using @AutoConfigureTestDatabase annotation because we want to run Integration tests with the MySQL database.
We have already configured the MySQL database in our Spring boot project so let's run Integration tests with the MySQL database.
Run Integration tests
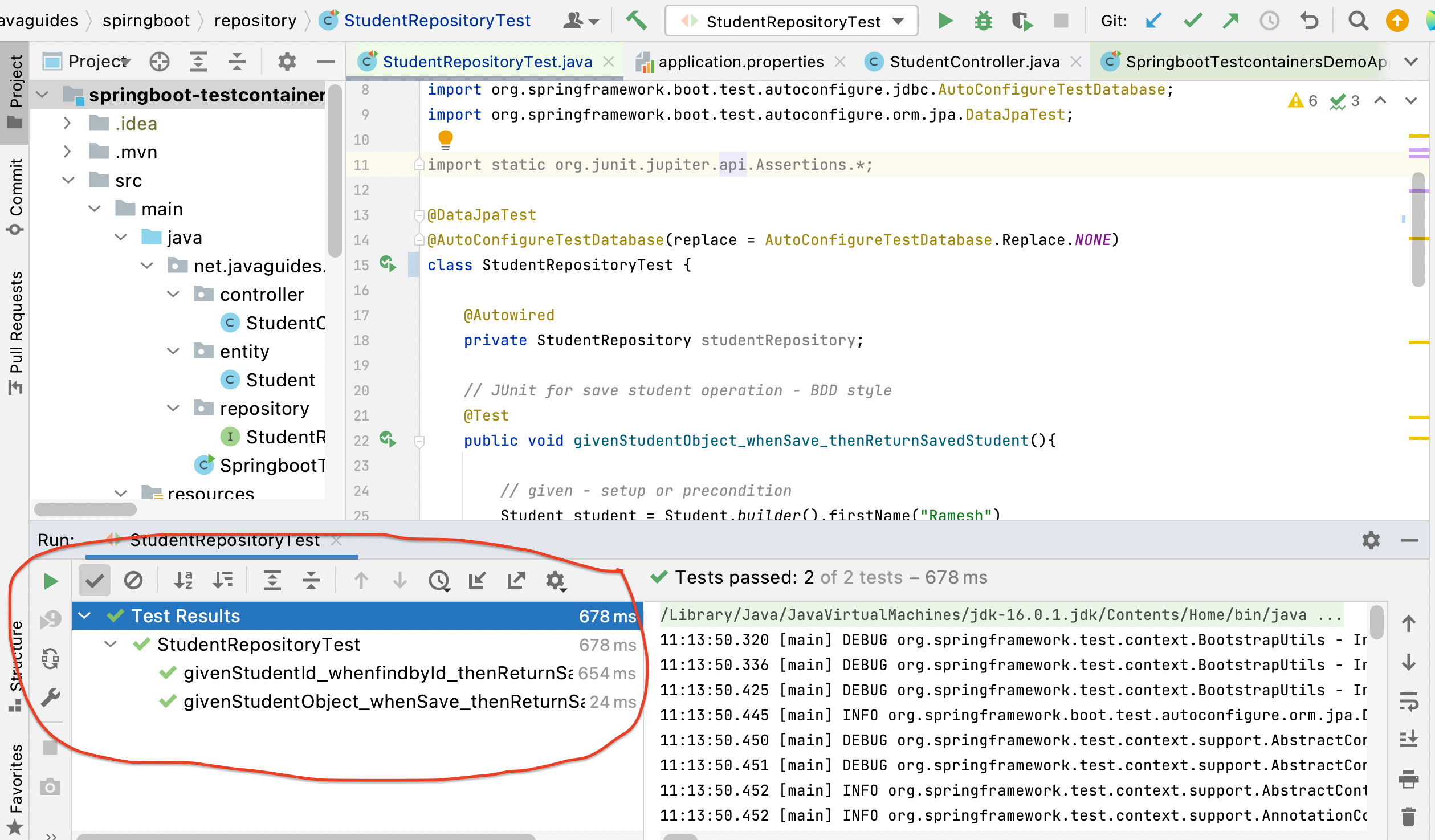
What is the problem with the Integration test that we have written?
A common problem when writing integration tests is the dependency on installed components (Ex: MySQL, RabbitMQ) where the integration tests are supposed to run.
In our case, our Integration tests depend on the MySQL database. Installing a specific version of the MySQL database in every machine where the integration tests are supposed to run takes a lot of time right.
Basically, our integration tests depend on external services (installing MySQL, Rabbit MQ, Redis, etc) to run the integration tests right then how to reduce this dependency - what will be the solution.
The solution is Testcontainers.
What is Testcontainers and how it solves the problem that we have already discussed in the previous tutorial,
Testcontainers is a Java library that supports JUnit tests, providing lightweight, throwaway instances of common databases, Selenium web browsers, or anything else that can run in a Docker container.
Testcontainer allows us to use Docker containers within our tests. As a result, we can write self-contained integration tests that depend on external resources.
Write Integration Tests for Data Access or Repository Layer using Testcontainers
Let's change the Integration test to use Testcontainers.
We just need to extend our StudentRepositoryTest class with AbstractContainerBaseTest class:
@DataJpaTest
@AutoConfigureTestDatabase(replace = AutoConfigureTestDatabase.Replace.NONE)
class StudentRepositoryTest extends AbstractContainerBaseTest {
// code goes here
}
Here is the complete code:
package net.javaguides.spirngboot.repository;
import net.javaguides.spirngboot.AbstractContainerBaseTest;
import net.javaguides.spirngboot.entity.Student;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.jdbc.AutoConfigureTestDatabase;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.DataJpaTest;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@DataJpaTest
@AutoConfigureTestDatabase(replace = AutoConfigureTestDatabase.Replace.NONE)
class StudentRepositoryTest extends AbstractContainerBaseTest {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
// JUnit for save student operation - BDD style
@Test
public void givenStudentObject_whenSave_thenReturnSavedStudent(){
// given - setup or precondition
Student student = Student.builder().firstName("Ramesh")
.lastName("fadatare").email("ramesh@gmail.com").build();
// when - action or the testing
Student savedStudent = studentRepository.save(student);
// then - very output
Assertions.assertNotNull(savedStudent);
Assertions.assertNotNull(savedStudent.getId());
}
// JUnit for save student operation - BDD style
@Test
public void givenStudentId_whenfindbyId_thenReturnSavedStudent(){
// given - setup or precondition
Student student = Student.builder().firstName("Ramesh")
.lastName("fadatare").email("ramesh@gmail.com").build();
Student savedStudent = studentRepository.save(student);
// when - action or the testing
Student studentDB = studentRepository.findById(student.getId()).get();
// then - very output
Assertions.assertNotNull(studentDB);
}
}
Note that we have created AbstractContainerBaseTest with Testcontainers logic in the previous tutorial
Run Integration tests using Testcontainers
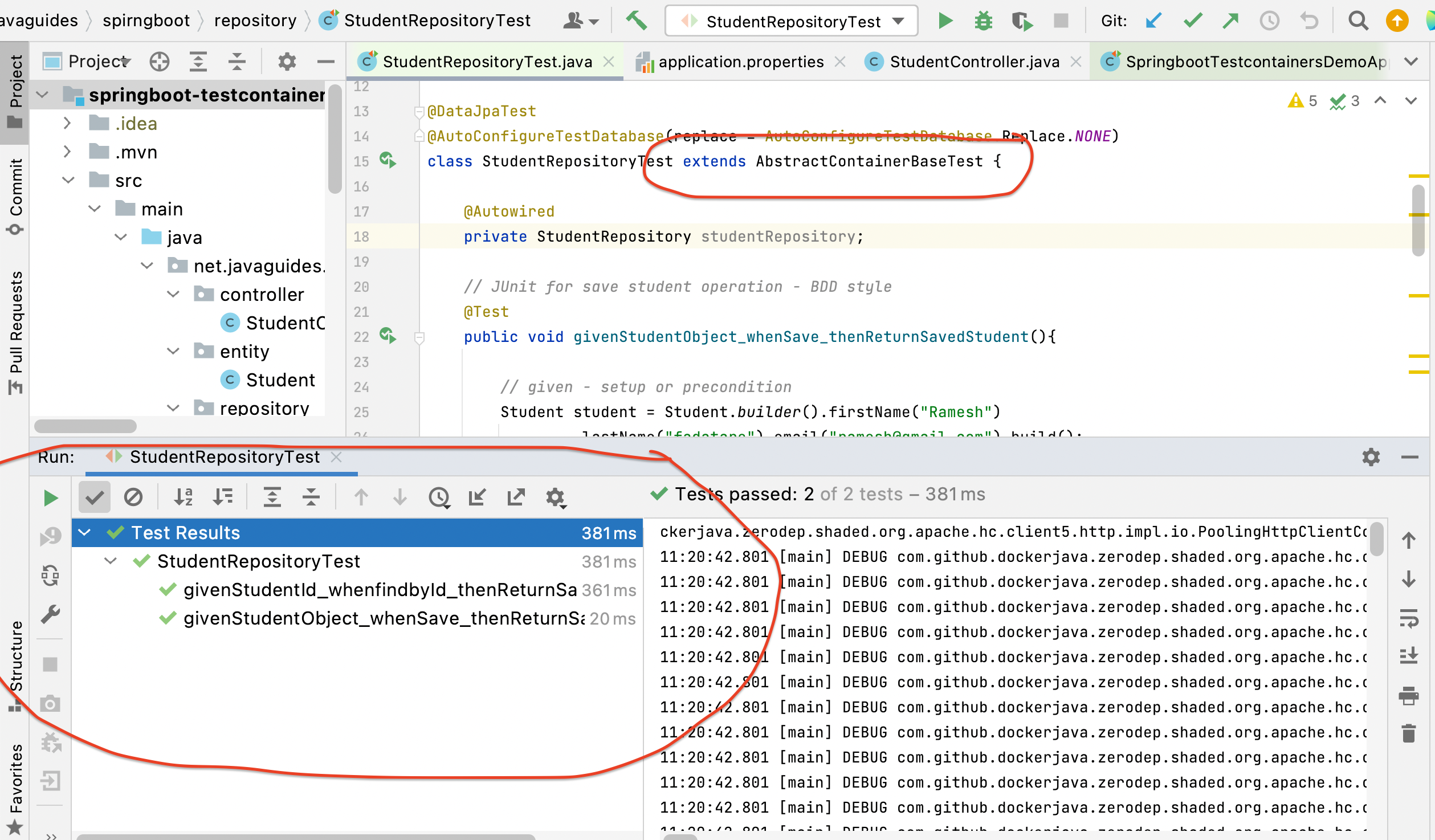
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have discussed how to perform Spring Boot Data Access or Repository layer Integration testing using Testcontainers.